3 Types of Insider Cybersecurity Threats
As the global workforce transitioned to remote working, an onslaught of cybersecurity threats hit small businesses and manufacture organizations which included insider cybersecurity threats. In a study conducted by Bitglass, 61 percent of businesses surveyed reported at least one insider-related cybersecurity incident in the last year.
This could be anything from negligent employees who lack cybersecurity training to rogue employees who facilitate a breach for personal gain. Employees could be working from home or on the manufacturing floor.
Consider the increase in frequency of insider cybersecurity threats and the severity of data breaches resulting from them, it goes without saying that all organizations need to take proactive steps to combat this serious security risk.
Before taking any preventative security measures, take a moment to understand who causes these risks and why. In this blog, we discuss all aspects of insider cybersecurity threats including the motivations behind them, potential actors, primary targets, consequences and more.
Table of Contents
3 Types of Insider Cybersecurity Threats
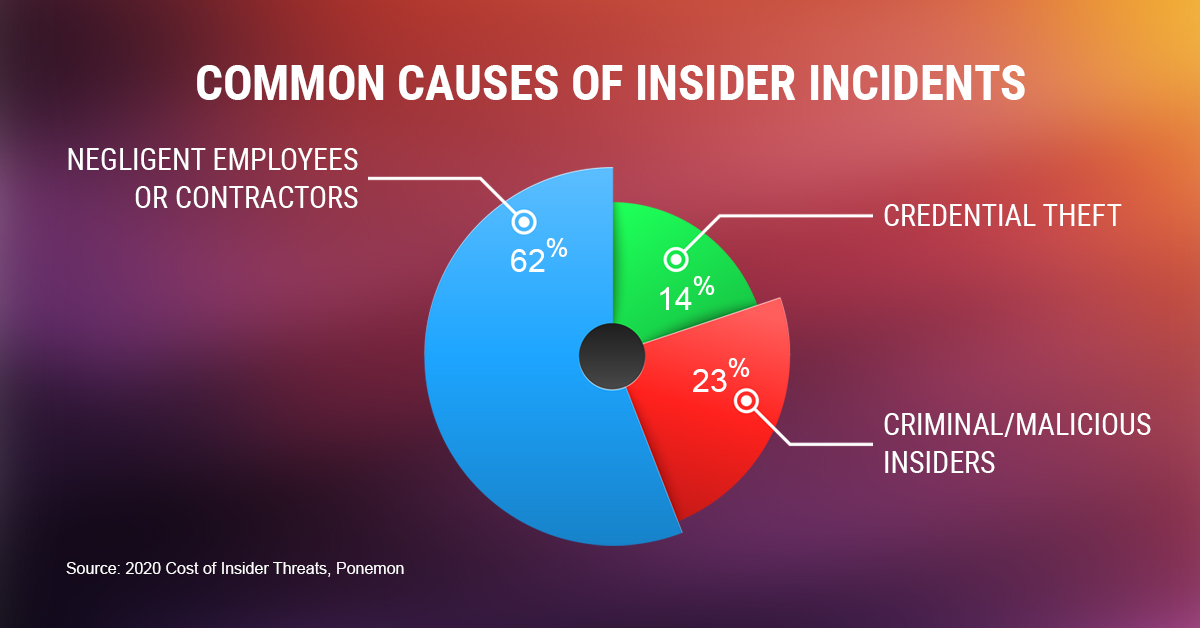
Anyone with access to critical information can pose a potential insider threat if the information is unknowingly or maliciously misused, resulting in a data breach. Businesses need to identify these actors if they want to curb insider threats effectively.
Insider threat types can be classified as follows:
- Negligent insiders – This may include careless executives or employees with access to privileged information. These insiders don’t have any motivation – money or otherwise. They are simply careless in their actions or may have fallen victim to a scam. For instance, in one particular incident involving an apparel manufacturer, a careless employee clicking one phishing link from his laptop was enough to compromise the entire network.
- Malicious insiders – These are insiders who intentionally abuse their credentials for personal gain. These actors have an advantage over external attackers since they have access to privileged information and are aware of the security loopholes. They may be motivated by monetary gain or may have a personal vendetta against the company.
- Contractors or vendors – Sometimes, even third-party vendors and contractors who have temporary access to an organization’s IT network can cause a data breach. The motivation in this case could also be money or vengeance. The US Army Reserves payroll system was once targeted in a similar attack, where a contractor who lost his contract activated a logic bomb to create a delay in delivering paychecks.
Motivation Behind Malicious Insider Threats
Malicious insiders are usually motivated by one or more of the following reasons:
- Money or greed – Most cases of non-negligent insider threats are motivated by money and personal financial gain. A greedy insider with access to restricted information is most often the culprit in this case. For example, two employees of General Electric stole the company’s intellectual property about calibrating turbines and started a competing firm with this information. After years of investigation, they were convicted in 2020.
- Revenge – Another familiar reason for insider threats involves revenge. Disgruntled employees, who believe they have been wronged by the company they once worked for, are usually behind this type of threat. In August 2020, a disgruntled former employee of Cisco deleted hundreds of virtual machines and caused about $1.4 million in damages to the company.
- Espionage – Many large organizations across the world have been victims of economic espionage from competing firms. This is mainly done to gain a competitive advantage in the market. A state-owned Chinese enterprise perpetrated espionage against American semi-conductor firm Micron by sending compromised insiders and stole valuable trade secrets.
- Strategic advantage – Intellectual property theft against large corporations is most often a result of trying to gain a strategic advantage in the market. Korean smartphone giant Samsung became a victim recently when its blueprint for bendable screen technology was stolen by its supplier.
- Political or ideological – There have been many documented cases of insider threats motivated by political or ideological factors. These cases often concern national pride or revenge against another nation for the attack.
Why Insider Cybersecurity Threats Are Dangerous
Insider threats often have a massive impact on your data, primary assets and your bottom line. On top of it all, these threats are often hard to detect and contain. A study by the Ponemon Institute estimates that it takes 77 days on average to contain insider threats once detected.
- Targets primary assets: Insider threats often target the primary assets of an organization including proprietary information, product information, business plans, company funds, IT systems and more.
- Results in huge costs: The same study by the Ponemon Institute estimated that the average cost of insider threats has increased 31 percent to $11.45 million in the last two years. These costs include downtime losses, loss of business transactions, loss of business opportunities and more.

Don’t Wait to Protect Your Business
Although the consequences of insider cybersecurity threats may be disastrous, you don’t have to face this problem alone. If you are wondering how you can mitigate these threats and prevent losses, we’ve got you covered. Reach out to us today to understand the different ways by which you can build a resilient cybersecurity posture against insider threats.
| Download our eBook to learn – How to Mitigate Insider Cybersecurity Threats |
Or
| Protect your business with us. |
Read this article, to learn more about putting a plan together that will protect your business.
Article curated and used by permission.
Data Sources:
- Bitglass 2020 Insider Threat Report
- https://www.zdnet.com/article/how-one-hacked-laptop-led-to-an-entire-network-being-compromised/
- https://www.theregister.com/2017/09/22/it_contractor_logic_bombed_army_payroll
- https://www.fbi.gov/news/stories/two-guilty-in-theft-of-trade-secrets-from-ge-072920
- https://www.bankinfosecurity.com/ex-cisco-engineer-pleads-guilty-in-insider-threat-case-a-14917
- https://www.justice.gov/opa/pr/prc-state-owned-company-taiwan-company-and-three-individuals-charged-economic-espionage
- https://edition.cnn.com/2018/11/30/tech/samsung-china-tech-theft/index.html
- IBM Cost of Insider Threats: Global Report 2020

Recent Comments